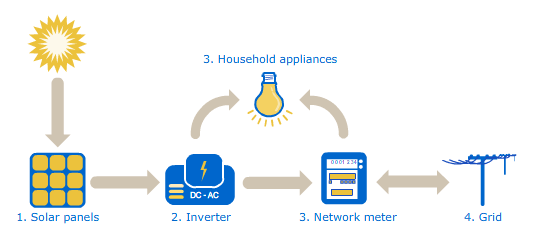
When the sunlight is absorbed by the solar panels, the panels create direct current (DC) electricity – like the electricity produced by a car battery. The direct current must be changed to alternating current (AC) electricity by the solar inverter.
The AC power produced by the solar inverter is first used by the home or business to power all the electrical appliances and loads. If the utility has net metering, any extra electricity can be exported to the grid for credit.
Without net metering, the excess electricity can be used to charge a battery that will power the home or building after sunset.
Download New Prairie Solar – Irradiance Guidelines!
